Select The Descriptions That Apply To Lipids
Lipids structure function made 5.4: how lipids work Lipids lipid macromolecules fatty glycerol acids triglyceride fats properties hydrogen biology molecule made fat acid triglycerides socratic biomolecules do three
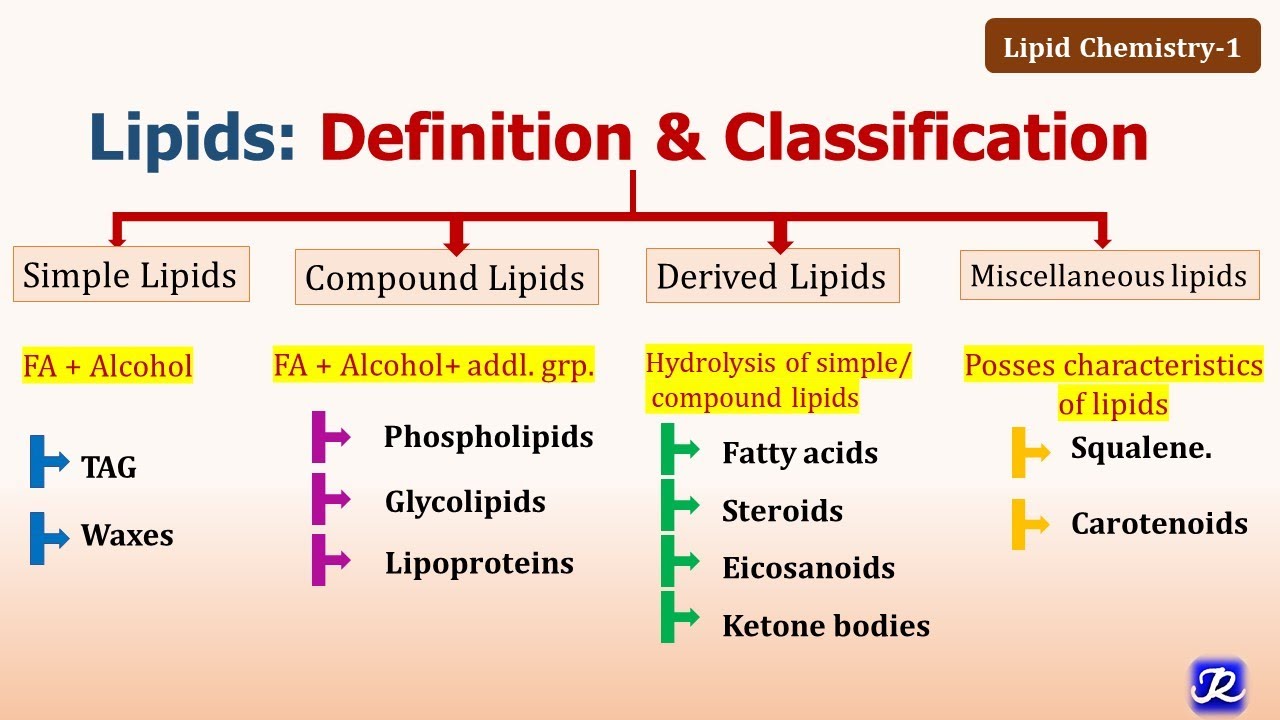
1: Lipids: Definition, Classification, functions |Lipid Chemistry-1
Dietary fat and plasma lipids Lipids structure properties functions classification types definition examples energy storage molecules cell plants used components insulation most Lipids fatty derived acids esters
Lipids fatty fats acids phospholipids triglycerides steroids biology which glycerol acid structures phospholipid molecular steroid triglyceride unsaturated saturated non chapter
Lipids fatsLipids academia 1.2.7 what are lipids made fromLipids fatty acids human phospholipids organic compounds cholesterol glycerol group groups prostaglandin essential prostaglandins phosphate important structure chemical steroids hydroxyl.
What are lipids and what are some of their common properties?Fatty acids saturated polyunsaturated lipids monounsaturated bonds fats points libretexts calabrese pageindex pressbooks differences unsaturation What are lipids? an introductionLipids lipid biochemistry functions.

Describe the different types of lipids.
3 uses of lipids in animals(pdf) lipid biosynthesis Biosynthesis lipid academia(pdf) lipids.
Lipids plasma dietary fat cambridge nutrition copyrightSolved part a what are some of the different kinds of 1: lipids: definition, classification, functions |lipid chemistry-1Uses of some lipids.

2.05: organic compounds essential to human functioning
.
.